Consulting phone:
135-3037-2041
(Mr.Wang)
Product introduction:
The cylindrical farad capacitor, also known as double-layer capacitor, gold capacitor and supercapacitor, is a chemical element developed from the 1970s and 1980s. Supercapacitors store energy through polarized electrolytes without chemical reaction, and the process of energy storage is reversible, which is precisely because this supercapacitor can repeatedly charge and discharge hundreds of thousands of times.
Series specification table:
Specification | characteristic | |||||||
Rated voltage VR | 3.0V.DC | |||||||
surge voltage | 3.15V.DC | |||||||
Capacity range | 1F-120F | |||||||
Operating temperature range | -40℃~+65℃ | |||||||
Product life | Normal temperature cycle life: At 25°C, the capacitor is charged and discharged 1 million times between the specification voltage and the half rated voltage with a constant current. Capacity attenuation ≤30% times, internal resistance change ≤3 times | |||||||
High temperature endurance life: under the condition of +65℃, the rated voltage is applied for 1000 hours. Capacity attenuation 30%, internal resistance change ≤3 times | ||||||||
Product performance table:
Product number | Rated voltage (V) | Nominal capacity (F) | Product size mm | Internal resistance | Working current (A)∆ T=15℃ | Peak current (A) | Leakage current (72hrs/µA) | High energy (Wh) | Energy density (Wh/kg) | functional density (kw/kg) | |
Outer diameter (ϕD) | Height (L) | ESRA C(mΩ/1KHz) | |||||||||
YKY3R0S105C01DSZ | 3.0 | 1 | 6.3 | 12 | 250 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 3 | 0.0013 | 1.67 | 1.20 |
YKY3R0S105C02DSZ | 3.0 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 180 | 0.26 | 0.83 | 5 | 0.0013 | 1.37 | 1.48 |
YKY3R0S205C02DSZ | 3.0 | 2 | 8 | 12 | 130 | 0.26 | 1.15 | 6 | 0.0025 | 2.75 | 1.48 |
YKY3R0S205C03DSZ | 3.0 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 120 | 0.43 | 1.74 | 8 | 0.0025 | 2.27 | 2.73 |
YKY3R0S335C04DSZ | 3.0 | 3.3 | 8 | 20 | 95 | 0.53 | 2.53 | 10 | 0.0041 | 2.84 | 2.57 |
YKY3R0S505C04DSZ | 3.0 | 5 | 8 | 20 | 80 | 0.59 | 3.41 | 12 | 0.0063 | 4.17 | 3.00 |
YKY3R0S505C06DSZ | 3.0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 70 | 0.77 | 3.93 | 15 | 0.0063 | 2.84 | 2.73 |
YKY3R0V705C05DSZ | 3.0 | 7 | 8 | 25 | 80 | 0.71 | 4.38 | 18 | 0.0088 | 4.61 | 2.84 |
YKY3R0V705C06DSZ | 3.0 | 7 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 0.81 | 4.95 | 18 | 0.0088 | 3.65 | 2.81 |
YKY3R0V106C06DSZ | 3.0 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 0.94 | 6.82 | 18 | 0.0125 | 5.1 | 3.67 |
YKY3R0V106C07DSZ | 3.0 | 10 | 10 | 25 | 40 | 1.27 | 8.33 | 20 | 0.0125 | 4.46 | 2.84 |
YKY3R0V106C09DSZ | 3.0 | 10 | 12.5 | 20 | 40 | 1.35 | 8.57 | 25 | 0.0125 | 3.57 | 4.11 |
YKY3R0V156C09DSZ | 3.0 | 15 | 12.5 | 20 | 40 | 1.35 | 10.59 | 30 | 0.0188 | 5.07 | 3.89 |
YKY3R0V156C10DSZ | 3.0 | 15 | 12.5 | 25 | 35 | 1.54 | 10.98 | 35 | 0.0188 | 4.36 | 3.59 |
YKY3R0V206C10DSZ | 3.0 | 20 | 12.5 | 25 | 35 | 1.66 | 13.64 | 50 | 0.0250 | 5.43 | 3.91 |
YKY3R0V256C12DSZ | 3.0 | 25 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 1.9 | 16.67 | 70 | 0.0313 | 5.21 | 3.60 |
YKY3R0V306C14DSZ | 3.0 | 30 | 16 | 30 | 20 | 2.53 | 20.45 | 80 | 0.0375 | 4.46 | 3.21 |
YKY3R0V506C15DSZ | 3.0 | 50 | 18 | 40 | 15 | 4.34 | 37.5 | 100 | 0.0625 | 4.7 | 4.06 |
YKY3R0V107C16DSZ | 3.0 | 100 | 18 | 60 | 12 | 5.85 | 57.69 | 260 | 0.1250 | 5.95 | 3.21 |
YKY3R0V107C17DSZ | 3.0 | 120 | 18 | 60 | 12 | 5.85 | 61.64 | 260 | 0.1500 | 7.14 | 3.21 |
Dimensions (unit: mm)
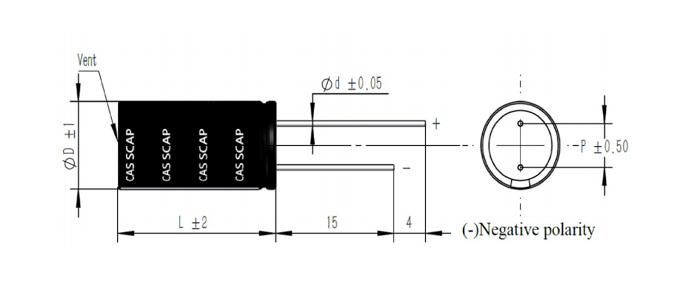
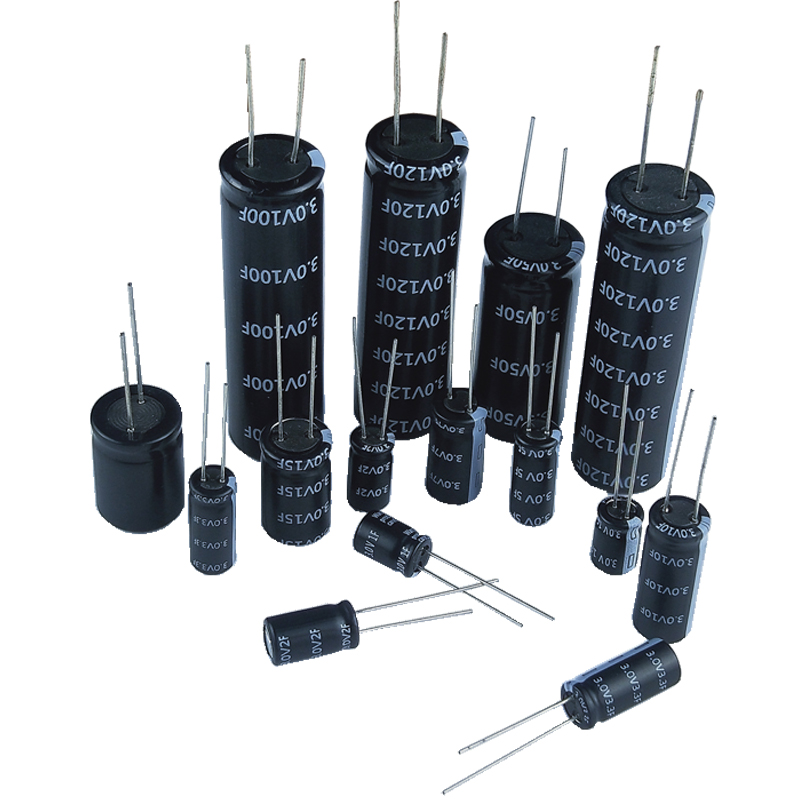
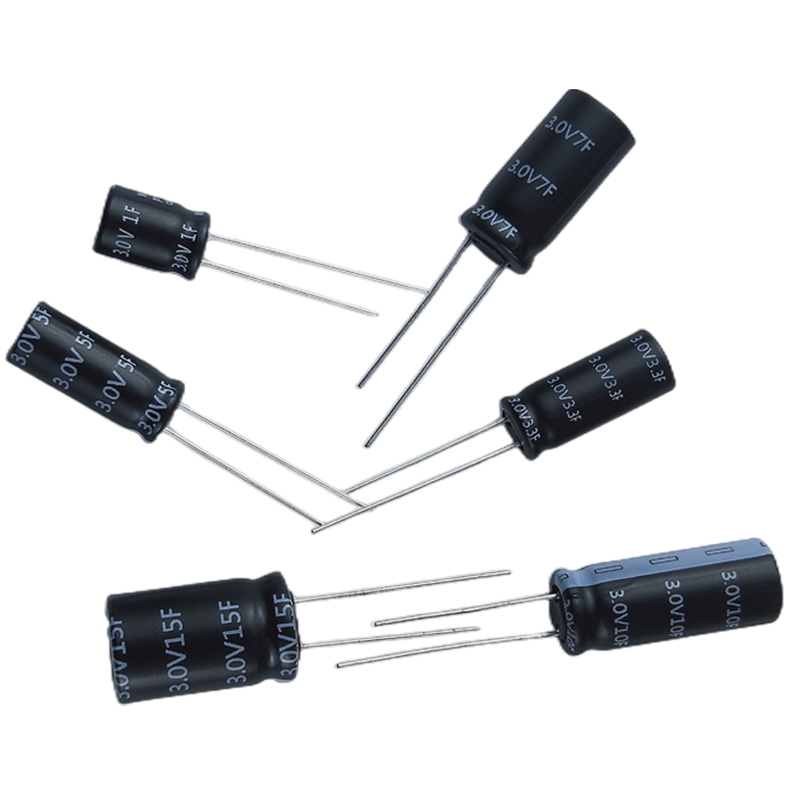
Product display:



Product advantages:

Application areas:
![1669272893126405.png [~]P`CO9T}7YQI[(0(}~%%E.png](http://en.szsyky.cn/data/upload/202211/1669272893126405.png)
testing method:
1. Electrostatic capacity test method:
(1) Test principle
The test of the electrostatic capacity of the supercapacitor is to use the method of constant current discharge of the capacitor, and calculate it according to the formula.
C=It(U1-U2)
In the formula: C - electrostatic capacity, F;
I-constant discharge current, A;
U1, U2 - use voltage, V;
t-Discharge time required for U1 to U2, S
(2), test procedure
Charge the capacitor with a current of 100A, charge the capacitor to the working voltage and keep the voltage constant for 10 seconds, then discharge the capacitor with a current of 100A, take U1 as 1.2V and U2 as 1.0V, record the discharge time within this voltage range, and the total cycle Capacitance, take the average value.
2. Stored energy test
(1) Test principle:
The test of supercapacitor energy is carried out by the method of discharging the capacitor with constant power to 1/2 of the working voltage with a given voltage range of the capacitor. The output energy W of the capacitor is obtained from the relationship between the constant discharge power P and the discharge time T, namely:
W=PT
(2) Test procedure
Charge the capacitor to the working voltage with a constant current of 100A, and then keep it constant until the charging current drops to the specified current (10A for traction type, 1A for start-up type), after 5 seconds of rest, discharge the capacitor with constant power to 1/2 of the working voltage, record Discharge time and calculate magnitude. Repeat the measurement 3 times and take the average value.
3. Equivalent series resistance test (DC)
(1) Test principle
The internal resistance of the capacitor is measured according to the sudden change of the voltage within 10 milliseconds of the capacitor disconnecting the constant current charging circuit. That is: in the formula:
R - the internal resistance of the capacitor;
U0 - capacitor cut off the voltage before charging;
Ui - cut off the voltage within 10ms after charging;
I - cut off the current before charging.
(2) Measurement process
Charge the capacitor with a constant current of 100A, disconnect the charging circuit when the charging working voltage is 80%, use a sampling machine to record the voltage change value within 10 milliseconds after the capacitor is powered off, and calculate the internal resistance, repeat 3 times, and take the average value.
4. Leakage current test
After charging the capacitor to the rated voltage with a constant current of 100A, charge the capacitor with a constant voltage for 30min at this voltage value, and then leave it open for 72h. During the first three hours, the voltage value was recorded every minute, and during the remaining time, the voltage value was recorded every ten minutes.
Calculate the self-discharge energy loss, SDLF=1-(V/VW)2, and the calculation time points are: 0.5, 1, 8, 24, 36, 72h.
Note: The voltage tester must have high input impedance to minimize the impact of discharge.
使用事项:
超级电容器不可使用在如下状态:
1) 超过标称温度的温度
当电容器温度超过标称温度时,将会导致电解液分解,同时电容器会发热,容量下降,
而且内阻增加,寿命缩短。
2) 超过额定电压的电压
当电容器电压超过标称电压时,将会导致电解液分解,同时电容器会发热,容量下降,
而且内阻增加,寿命缩短。所以降低使用电压可提高使用寿命。
3) 逆电压或交流电压的加载
1.周围温度对超级电容器的影响
超级电容器的使用寿命受使用温度的影响,一般情况下,使用温度提升10℃,超级电容器的寿命会缩短一半,请尽量在低于最高使用温度的低温环境下使用。超过最高使用温度使用的话,可能会造成特性急剧劣化,破损。
超级电容器的使用温度不仅要确认设备周围温度,内部温度,还要确认设备内发热体(功率晶体管、电阻等)的放射热,纹波电流引起的自行发热温度。此外,还请勿将发热体安装在超级电容器的附近。
2.请按电容器的正负极标识正确使用。
3.请避免在以下环境中使用超级电容器。
a) 直接溅水、盐水及油的环境、或处于结露状态、充满着气体状的油分或盐分的环境。
b) 充满着有害气体(硫化氢、亚硫酸、氯、氨、溴、溴化甲基等)的环境。
c) 溅上酸性及碱性溶剂的环境。
d) 阳光直射或有粉尘的环境。
e) 遭受过度的振动及冲击的环境。
4.在焊接过程中要避免使电容器过热(1.6mm的印刷线路板,焊接时应为260℃,时间不超过5s)。
5.请避免在超级电容器的引出极间或连接板焊点间进行电路配线。
6.过电压及超过工作温度范围等超出额定条件使用时,可能导致压力阀动作,电解液会喷出。因此,请采用已考虑到此异常状况可能发生的设计方法。
7.快速充放电时,充电开始时、放电开始时,会产生由内部阻抗导致的压降(也叫IR降),所以,请采用已考虑到电压变化幅度的设计方法。
8.功率型大容量产品(约10F以上产品)充电状态下如果端子短路,会有数百安培的电流流过,危险。请不要在充电状态下进行安装和拆卸。
9.不要把电容器放入已溶解的焊锡中,只在电容器的导针上粘焊锡。不可让焊接用焊棒接触电容器热缩管。
10.安装后,不可强行扭动或倾斜电容器。
11.超级电容器串联使用时,存在单体间的电压均衡问题。